Thanks to validation exercises undertaken within the SESAR programme, a new, more efficient arrival procedure at a high altitude has been put in place at Paris-Charles de Gaulle airport for integrating inbound flights using a Point Merge system.
Point Merge involves setting a merge point in the airspace near the airport and then drawing arcs further out that are centred on the defined point. An inbound aircraft is placed in one of the arcs and then directed towards the merge point, on a straight course. The next aircraft follows the same procedure, allowing the routes of the arriving traffic to ‘merge’ on the same merge point with accurate and optimum sequencing and spacing.
The procedure impleme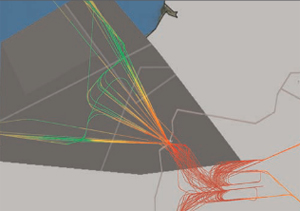 nted in Paris uses a merge point located approximately 40 NM from the airport. When traffic density is high, the air traffic controller instructs the pilot to fly on the arc until he is instructed to turn inbound to the merge point when the right spacing from the preceding aircraft has been attained. Here the airspace required a complex re-design since the merge points and the arcs flown by aircraft are much bigger.
nted in Paris uses a merge point located approximately 40 NM from the airport. When traffic density is high, the air traffic controller instructs the pilot to fly on the arc until he is instructed to turn inbound to the merge point when the right spacing from the preceding aircraft has been attained. Here the airspace required a complex re-design since the merge points and the arcs flown by aircraft are much bigger.
With Point Merge, aircraft are already in the right landing order when leaving the point merge arc. Compared to a normal procedure, this allows the aircraft to remain at higher altitude for longer and descend on a continual path at a later stage to the initial approach fix, which greatly decreases noise impact.
Point Merge is widely considered as one of the most important tools for allowing the aviation sector to reach its safety, capacity and environmental targets. The Pont Merge procedure results in a reduction in radio frequency usage thus reducing controller workload. The system also results in greater flight efficiency, since more flights can be managed simultaneously while they are in continuous descent, even during heavy traffic periods. These benefits have been validated by SESAR and are now clearly visible at Paris Charles de Gaulle.
Managed by Direction des Services de la Navigation Aérienne (DSNA), the French Air Navigation Service Provider, the SESAR project ran two validation exercises in 2012. Participants in the exercises included Air France, Belgocontrol and Eurocontrol.
In SESAR, success can only be achieved through stakeholder participation. In line with the SESAR vision, the project saw the training of some 200 controllers at Paris ACC in order to make this concept a reality, and close cooperation with airline companies was maintained throughout the procedure’s development and implementation.
Speaking about the new procedure, Kevin, an air traffic controller at Paris ACC, said: “By increasing safety, Point Merge gives more time for controllers to better manage unexpected events and to improve the service provided.”
DSNA Director, Maurice Georges also commented on the potential of the new procedure:“I would like to congratulate all those who contributed to the successful achievements of this project, a first in the Core Area which deals with the most dense and complex traffic at the heart of Europe. This more efficient organisation of our air traffic management offers quality and competitive services to all our operational partners and customers.“
